This page by David Mark Papkin contains useful Linux links
Best Linux Distributions That are Most Suitable for Beginners
10 of the Most Popular Linux Distributions Compared
10 Best and Most Popular Linux Desktop Environments of All Time
The Difference Between Fedora, Redhat, and CentOS
What is the relationship between Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux?
Red Hat and the CentOS Project Join Forces to Speed Open Source Innovation
Understanding the Color Code of Linux files
GNU General Public License (GPL) v2.0
Is Linux kernel free to modify?
https://wiki.centos.org/FAQ/CentOS7
How to change runlevel on Centos 7
Learn Linux, 101: Runlevels, boot targets, shutdown, and reboot
Check what Debian version you are running on your Linux system
Setup Local Yum Repository on CentOS / RHEL / Scientific Linux 6.4
Ansible
You can find sample playbooks here
https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/network/getting_started/first_playbook.html
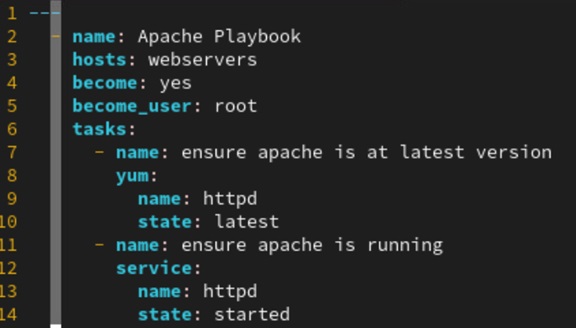
ANSIBLE – SETTING UP APACHE WEB SERVER
The links below are from Redhat.
https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/ansible-callback-plugins
ansible.builtin.service module – Manage services
How to setup a Webserver using Ansible
1. Uncomment the ##[webservers] section in /etc/ansible/hosts.
2. Uncomment the IP address(es) of the remote hosts you want to install Apache webserver on in the webservers section
3. Create a yaml file to be used to run a playbook. Example apache.yml. Please note the first line is 3 dashes. Spacing is CRUCIAL in ansible YAML files. DO NOT USE TAB key! Highly suggest using vim with modified .vimrc file (SEE BELOW) or Visual Studio Code with Ansible extensions installed (easiest since shows spacing graphically)
Install VIM .
a) dnf -y install vim
b) cd ~ or cd
c)To make vim able to detect YAML syntax errors, edit the .vimrc file command below:
vim .vimrc
Put the following 2 lines in .vimrc and save and exit.
autocmd FileType yaml setlocal et ts=2 ai sw=2 nu cuc
d) vim apache.yml
4. Run the playbook
ansible-playbook apache.yml -i /etc/ansible/hosts
5. Test to see that the remote webserver(s) are installed on the remote host.
ssh root@192.168.1.100
systemctl status httpd
Backup
55187 Linux Backup lab by David Papkin
Commands
Firewall
https://phoenixnap.com/kb/iptables-tutorial-linux-firewall
CentOS / Redhat Iptables Firewall Configuration Tutorial
Ubuntu Iptables: How to Control Network Traffic Using iptables?
Graphical Admin tools
Managing systems using the RHEL 8 web console
How to Install Webmin on CentOS 7
How to Install Latest Webmin on Debian 10/9/8
Web-based interface for system administration
Hypervisor
Downloads – Oracle VM VirtualBox
How to Install Apache Server and Set Up Virtual Hosts on Ubuntu 22.04
https://www.wikihow.com/Install-VirtualBox
How to Fix “VT-X Is Not Available (verr_vmx-No-Vmx)” Error in VirtualBox
WSL
Install Linux on Windows with WSL
https://documentation.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install
VirtualBox
How to Install Linux in VirtualBox
KVM
How To Install KVM Hypervisor on Ubuntu 22.04|20.04
Hyper-V
Installing CentOS 7 using Hyper-V
CentOS Linux on Hyper-V – The Complete Guide
Centos 7 installation in hyper-v on windows 11
VMware
Instructions To Install CentOS Linux 9 On VMware Workstation
Step‑By‑Step Procedure To Install CentOS Linux On VMware Workstation
Installing CentOS 9 on VMware Workstation 17
MAC Hypervisor
List of iso that prepared but can install others https://mac.getutm.app/gallery/
Visit the official CentOS website download page
https://www.centos.org/download/
Kali downloads
https://www.kali.org/get-kali/#kali-platforms
Rocky Linux
Ubuntu downloads
Monitoring
https://www.tecmint.com/command-line-tools-to-monitor-linux-performance/
https://www.thegeekstuff.com/2011/12/linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
https://www.cyberithub.com/steps-to-install-iostat-mpstat-command-on-linux-rhel-centos-7-8/
How to install htop on CentOS 8
How to install ioping on Ubuntu
How To Check For Open Ports in Linux With netstat, lsof And nmap
See Bandwidth Usage Per Process With Nethogs Tool
How to Monitor Network Traffic using nethogs
NetHogs – Monitor Per Process Network Bandwidth Usage in Real Time
Networking
What happened to eth0? Predictable Network Interface Names
How can I change the default “ens33” network device to old “eth0” on Fedora 19?
Change default network name (ens33) to “eth0” in Centos7/RHEL7
How to change a network interface name on CentOS 7
Password reset
How to Reset Forgotten Ubuntu Password in 2 Minutes
How To Recover Root Password In RHEL/CentOS In 5 Minutes?
Reset root Password Centos/Redhat (challenging)
Patching
Ultimate guide to linux patch management
Patch Management Best Practices
10 Linux Hardening & Security Best Practices
40 Linux Server Hardening Security Tips [2021 edition]
Permissions
Linux permissions: SUID, SGID, and sticky bit
Controlling file permissions with umask
Recycle Bin
Trash-cli – A Trashcan Tool to Manage ‘Trash’ from Linux Command Line
Scripting
- Create this sample.sh file with vim or nano
- chmod 700 sample.sh
- ./sample.sh
- cat file1.txt
This will output all commands to file1.txt
sample.sh
#!/bin/bash
top -n 2 > file1.txt
SELinux
A sysadmin’s guide to SELinux: 42 answers to the big questions
Shell
🔹 Popular Online Linux Shells
| Service | What It Offers |
|---|---|
| JSLinux | A full Linux emulator in your browser (created by Fabrice Bellard). Boots real Linux with busybox tools. |
| Copy.sh | Emulates x86 PCs and can run Linux, Windows 95, FreeDOS, etc., all inside the browser. |
| Webminal | Online Linux terminal designed for training. Free account required, includes practice exercises. |
| LinuxZoo | Interactive Linux lab environment for learning, with real VM access after signup. |
| Katacoda (O’Reilly Playground) (was Katacoda) | Interactive scenarios for Docker, Kubernetes, and Linux CLI. Many tutorials are free. |
| TutorialsPoint Coding Ground | Provides online Linux terminal and IDE for multiple languages. |
| replit.com | While aimed at coding, you can run a Linux shell environment (Ubuntu-based). |
| OverTheWire Bandit | Gamified Linux shell access over SSH for learning commands and security basics. |
Software packages
How To Set Up Local Yum Repositories On CentOS 7
CentOS / RHEL : How to create and host yum repository over httpd
Configuring Yum and Yum Repos (REDHAT Docs)
Security
Storage
GRUB 1 bootloader – Full tutorial
GRUB 2 bootloader – Full tutorial
Understanding File System Superblock
Linux LVM Logical Volume for CentOS 7 / RHEL 7
You can monitor RAID devices multiple ways as in:
$ sudo mdadm --detail /dev/md0
$ cat /proc/mdstatOne can also use mdmonitor which requires configuring /etc/mdadm.conf.
The command:
$ sudo mdadm --detail /dev/mdX
will show the current status of the RAID device /dev/mdX. Another way to do this is to examine the /proc filesystem:
$ cat /proc/mdstat
Timezones
Q How to set the timezone to Singapore?
A timedatectl set-timezone Asia/Singapore
timedatectl status
User Mgmt
Assorted
GNU General Public License (GPL) v2.0
Is Linux kernel free to modify?
How to Configure ACL(Access Control Lists) in Linux FileSystem
Q & A
Q How to check resource usage for a server twice per hour?
A vmstat 1800 2
Q How to tell the status and current RAID level of your Linux software RAID array?
A
sudo bash -c mdadm –detail –scan
cat /proc/mdstat
Q
How to check your RAID volume md0?
A
mdadm –query /dev/md0
Q
How to check that status of an individual disk in a RAID array?
A
mdadm –examine /dev/sdb2 (if sdb2 is the disk you want to check)
How to list logical device in Logical Volumes in lv012?
A
lvdisplay -v /dev/vg00/lvol2Q How to troubleshoot in Linux?
A
The following list represents the basic steps in a troubleshooting methodology:
• Identify the problem.
• Determine the scope of the problem.
• Establish a theory of probable cause/question the obvious.
• Test the theory to determine the cause.
• Establish a plan of action.
• Implement the solution or escalate the issue.
• Verify full system functionality.
• Implement preventive measures.
• Perform a root cause analysis
Q
How to check a physical volume that is using Logical Volume Manager?
A
pvdisplay /dev/ssd3
Q How to show the usage of process that are consuming network bandwidth?
A
a) You can use the nethogs utility.
ex nethogs -a
or
nethogs -i ens33 or whatever interface you want to get usage stats from.
b) you can use vnstat utility
vnstat -i ens33
vnstati -s -i ens33 -o vnstatreport.png
Q How to know what ports a server is listening to?
A lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN
Q How to see what active connections from the Internet?
A netstat –listen
Q How to use iptables
A
a) Display Your Firewall status
iptables -L -n -v
b) Display firewall with line numbers
iptables -n -L -v –line-numbers
c) Display INPUT or OUTPUT chain rules
iptables -L INPUT -n -v
iptables -L OUTPUT -n -v
d) Stop / Start / Restart the Firewall
service iptables stop/start/restart
e) Drop all incoming / forwarded packets, but allow outgoing traffic
iptables -P INPUT DROP
iptables -P FORWARD DROP
iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT
iptables -A INPUT -m state –state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
iptables -L -v -n
Q How to install an Apache web server on a Linux Virtual Machine?
A
-
Create a new virtual machine and select a Linux distribution, such as Ubuntu or Centos.
-
Click on the “Create” button and select the following settings:
- Operating System: Linux
- Version: Ubuntu (64-bit)
- Name: Your web server name
- Memory: 2 GB
- Hard Disk: 20 GB
-
Click on the “Create” button to create the virtual machine.
-
Once the virtual machine is created, start it up.
-
The virtual machine will boot up and you will be presented with a screen asking you to select a language. Select your language and click on the “Continue” button.
-
The virtual machine will now start installing the operating system. This process may take a few minutes.
-
Once the operating system is installed, you will be presented with a login screen. Enter the username and password that you created during the installation process and click on the “Log in” button.
-
Once you are logged in, open a terminal window.
-
Install the Apache web server package by running the following command:
sudo apt install apache2
or
dnf install httpd- Type echo “Welcome to my website” >> /var/www/html/index.html
- The Apache web server will be installed and started automatically. You can verify this by opening a web browser such as Firefox and navigating to the http://<your IP address>of the virtual machine or http://localhost
- To add a website to the web server, create a new directory in the
/var/www/htmldirectory and add your website files to it. -
To update the software packages on the web server, run the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
This will update all of the software packages on the web server to the latest versions.
Security
6 Steps to Assess your Network Security
Follow these six steps to assess the vulnerability of your network:
Step 1: Identify and understand the way your business is organized and operates
- Most businesses rely on collaboration between representatives from their internal business units, legal teams, and finance departments to coordinate with IT professionals regarding their exact network needs. Consider issues such as client or customer privacy, regulatory compliance, business processes, and competitive positioning within your industry.
Step 2: Locate the applications and data that are used during the business process
- Identify which of these are sensitive and what information is at risk in the event of a privacy breach.
Step 3: Search for hidden data sources that may allow easy access to secure information
- This is especially important if there is cloud-based access to private data or access across multiple platforms, including smartphones and tablets.
Step 4: Identify both virtual and physical servers that run applications necessary for your business operations
- These servers may not be protected and may allow access to sensitive information without you knowing it.
Step 5: Keep track of what security measures are already in place
- Your network protection may already include specific policies, firewalls, virus detection, VPNs, disaster recovery, and encryption. It’s important to understand the capabilities of your current security measures in order to properly address any vulnerabilities.
Step 6: Scan your network for vulnerability
- The results of this scan will give you confirmation of your network’s security. Should a virus or vulnerable area be identified, you will need to develop a network security strategy, possibly with the help of an MSP. There are many tools to scan for vulnerabilities.
IS Standard and Frameworks
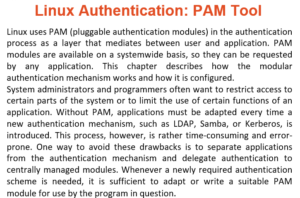
Linux Authentication: PAM Tool
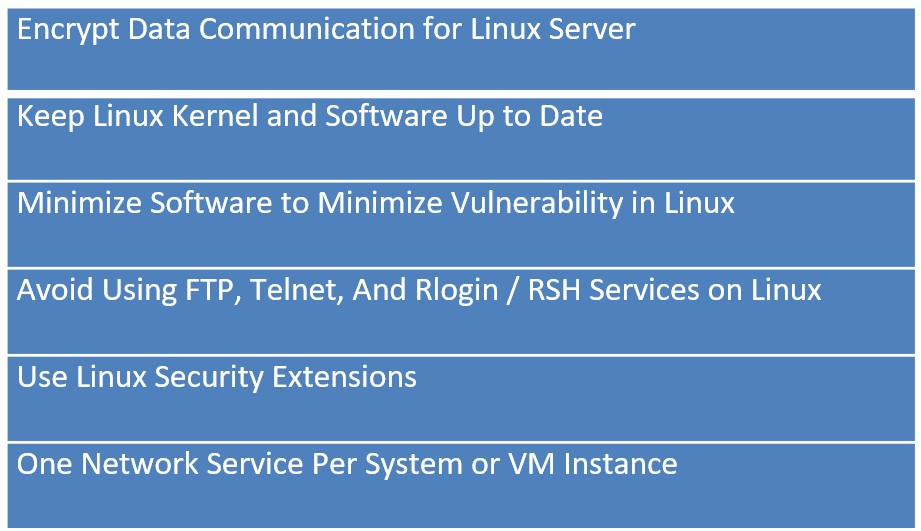
Name some Linux Security Tips and Checklist
A

Download
Upload
End of David Mark Papkin linux links